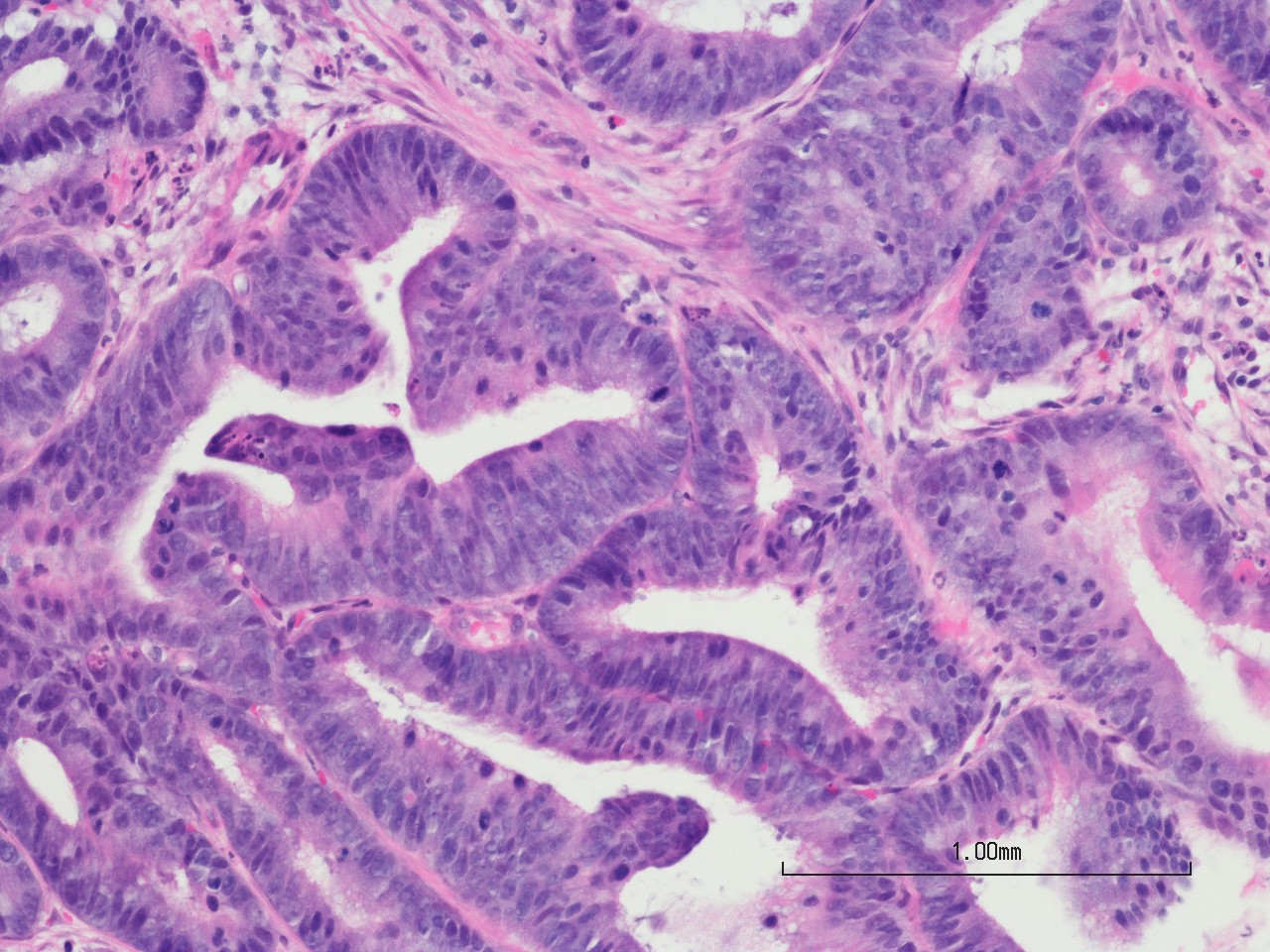
How Colon Cancer Starts
Colon cancer starts in polyps. You may be more likely to develop polyps than other people, especially if you have a family history of polyps or colon cancer.

If cancer runs in your family, be especially careful not to over-imbibe.
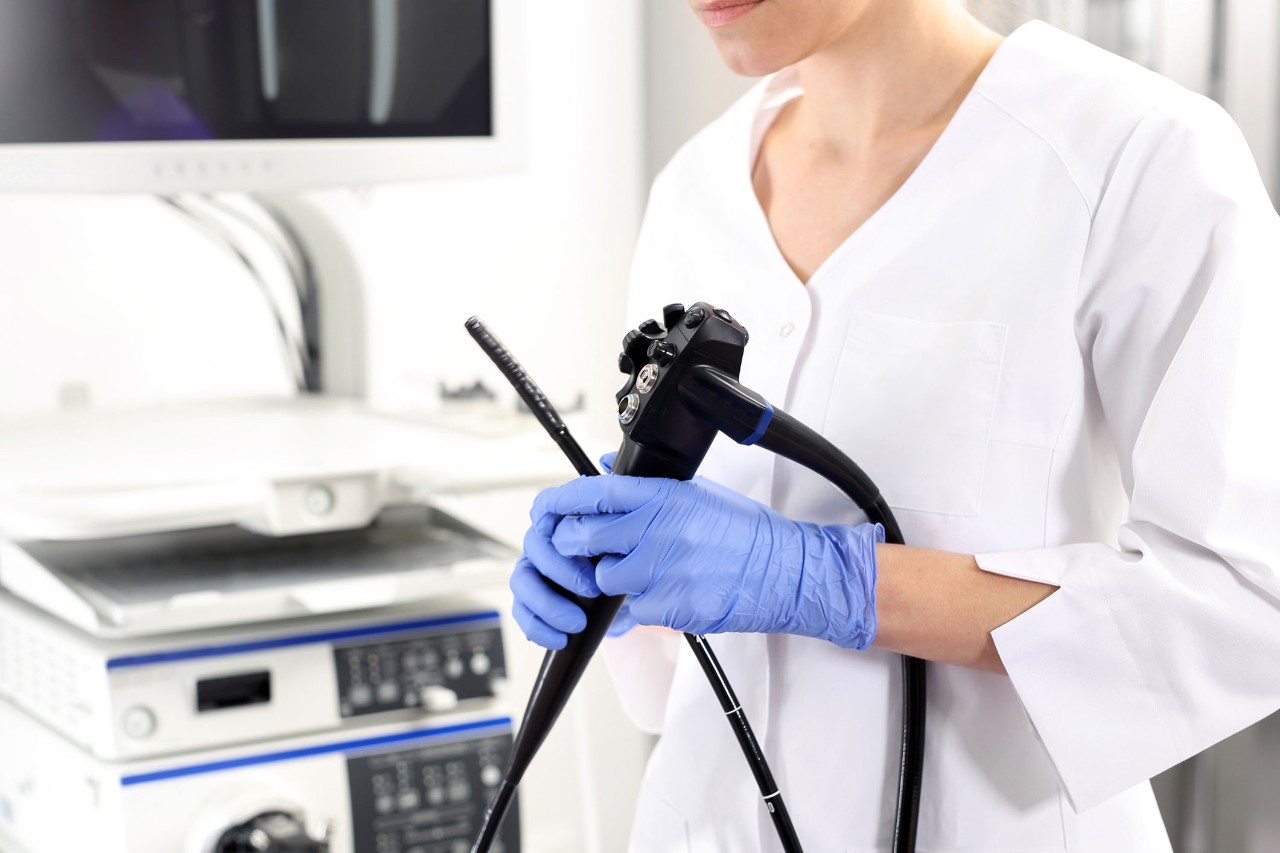

What is a colonoscopy? This procedure detects early signs of colon, or colorectal, cancer that make your chances of recovery and survival more likely.

Most colon polyps are benign, but some develop into colorectal cancer. There are usually no symptoms of colon polyps, but see your doctor if they do occur.

The American Cancer Society now recommends that people with an average risk for colorectal cancer start getting screened at age 45.

Bowel cancer can be deadly if caught late. Regular screenings and seeing your doctor ASAP if you recognize any bowel cancer symptoms can save your life.

Though colon cancer can develop at any age, your medical history, lifestyle choices, and family history all affect your risk factors for colon cancer.

There are various treatment choices for colon cancer. Which may work best for you? Your treatment depends on the type, size, location, and stage of your cancer.

During colorectal surgery, often a colectomy, parts of the colon or rectum are surgically removed (sometimes the entire rectum). Here’s what you should know.

Always follow the instructions you get from your healthcare providers, and contact them with any questions once you go home after surgery for colon cancer.

During an ileostomy, healthcare providers either remove or disconnect your colon (large intestine) and sometimes part of the last section of your ileum.

While they can be lifesaving — overuse of antibiotics may cause health problem, including possibly increasing the risk for precancerous colon polyps in the colon.