What Is Rheumatoid Arthritis?
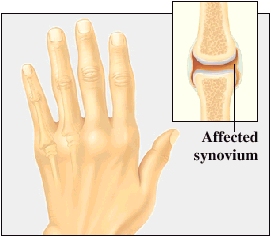
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a disease that affects the synovium, the lining of the joints. This causes pain, swelling, and stiffness. Left untreated, rheumatoid arthritis may damage joints so badly that they no longer function. This disease appears most often in young-adult to middle-age women.
YOU MIGHT ALSO LIKE: Solving the Riddle of Rheumatoid Arthritis
What causes RA?
RA is an autoimmune disorder. This means the immune system, which normally protects the body, actually causes harm. In RA, the immune system attacks the joint lining. The reason for this is unknown. Researchers believe it is a combination of genes (what is inherited from parents) and environment (for example, having infections from viruses or bacteria). Also, people who smoke or are overweight have an increased risk of developing RA.
What are the symptoms of RA?
Rheumatoid arthritis can affect most joints. The hands, wrists, elbows, knees, and balls of the feet are common sites. This disease often affects the same joint on both sides of the body. Symptoms may include:
- Tender, swollen inflamed joints. They may also look red and feel warm.
- Stiff joints. Long periods of rest or using a joint too long or too hard can make stiffness worse.
- Joints that have lost normal shape and motion.
- Feeling tired.
How is RA diagnosed?
To diagnose rheumatoid arthritis, your health care provider will ask you a lot of questions about your medical history and current symptoms. He or she will examine you, paying close attention to your joints. You will also have blood tests and X-rays. Your provider will likely recommend that you see a rheumatologist, an arthritis specialist.
Updated:
March 27, 2020
Reviewed By:
Hollaway, Beth, RN, M.Ed, MMI board-certified, academically affiliated clinician